Summary
Responsible Investing & Performance: Continuing earlier studies
Article published December 9, 2021 and Video recorded on January 19, 2022
Acting as a responsible financial institution is a founding pillar of Amundi’s corporate strategy. This is demonstrated not only through our pledge to make ESG investing standard throughout our whole product range, but also through our commitment to ESG research in order to fully understand the responsible investment landscape.
This paper marks the latest update in our series exploring the impact of ESG investment on asset pricing in stock markets. The previous papers*, covering the periods 2010-2019, found that:
- ESG investing tended to penalize both passive and active ESG investors between 2010 and 2013.
- In contrast, ESG investing was a source of outperformance from 2014 to 2017 in Europe and North America, and was even becoming a beta strategy in the Eurozone.
- More recently the trends between North America and the Eurozone have somewhat diverged with ESG performance in North America lagging the sustained advances made in the Eurozone.
- In 2018-2019, a move became apparent from bestin-class selection policies to the implementation of more active strategies to integrate a dynamic view of ESG scores.
- The social pillar came to the fore in 2018-2019 after lagging from 2014-2017, likely due to growing concern for social themes such as rising inequalities.
Since the last update in 2019, we have lived through a global pandemic that profoundly reshaped the global economy and society, in addition to an eventful change of leadership in the United States.
This paper, covering the period June 2019-June 2021, continues our work looking at trends in the North American and the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) universes, but also expands its horizons to the Emerging Asia market for the first time.
Key findings
1. Joe Biden’s election was originally predicted to energize ESG investing
The so-called “Biden effect”, which it was assumed would drive ESG performance in North America, was actually anticipated much earlier by investors in the light of increasing ESG consciousness. Positive performance across all three pillars is evident in the market well before the election.
2. But it nonetheless set off a “Green momentum”
Focusing on the environment pillar, it can be argued that the election of Joe Biden fuelled a trans-regional “green momentum” as the postelection period showed a clear outperformance from the Energy and Emissions sub-pillar. The “green momentum” of the election translated into investors better integrating companies’ CO2eq emissions when carrying out stock selections.
3. Rise of the Social pillar in North America
The first quarter of 2020 saw the Social pillar outperform other ESG metrics in North America. Analysing the sub-pillars making up the Social pillar across the wider period, it can be observed that this development has been dominated by Working Conditions, a trend which can likely be linked to the Covid-19 crisis and subsequent instability in labour markets. The effects of Covid-19 hindered the Social pillar’s dominance, but it has begun to regain importance again more recently, although not yet returned to pre-crisis levels.
4. Governance most robust pillar during crisis
Prior to the pandemic, the three regions studied exhibited differing drivers of ESG performance, but the trends converged dramatically at the heights of the Covid-19 crisis when the Governance pillar emerges strongly as the most resilient pillar in all regions. Companies with strong governance practices markedly outperformed other pillars.
5. Better governance = lower cost of capital
In North America, the Covid-19 crisis sparked a huge need from companies for extraordinary external financing which was ultimately met by the credit market. Governance became the most decisive factor as firms with good governance practices increased their advantage through a lower cost of capital.
6. Emerging Asia is the outright ESG winner
In extending our analysis to the Emerging Asia region, we find that the region has exhibited the strongest returns on all ESG aspects since November 2020 of all the three regions studied. Governance performed steadily across all periods confirming investors’ particular focus on this area, and more broadly, the critical role of governance in emerging markets. An interesting phenomenon in particular was remarked in Emerging Asia around the Ethics sub-pillar, which was found to be the largest contributor to the governance return and highlights a growing concern on this theme, not solely limited to the impacts of the pandemic.
Context of study environment
It is important to note that this study covered a period of unprecedented disruption. The Covid-19 outbreak in early 2020 not only shattered the markets worldwide, but also population and trade movement. The implications of these are still causing significant headwinds on today’s markets. Covid-19 also fostered significant disruptions to business models and accelerated changes in collective attitudes towards numerous ESG themes. The US political scene simultaneously paved the way for potential policy U-turns. Nevertheless, uncertainty remained over the outcome of the presidential race and whether Biden would be able to effectively implement the promised ESG-focused policies.
Did Biden’s election generate an ESG effect in North America?
Our previous studies have shown that ESG investing began to be rewarded by markets in 2014. Since then, awareness around environmental, social and governance challenges have steadily increased, supporting the theory that ESG should increase in importance in the asset pricing of firms, while benefiting all stakeholders.
However, as already observed in our previous papers, advances in ESG and their corresponding impact on financial markets are at different stages across the world, a phenomenon notably illustrated by the transatlantic divide. A possible justification for this divergence had been the Trump administration’s conflicting environmental stance. It could be expected therefore that the election of Biden would lead investors to assume deeper integration of ESG in North America that would be triggered by the new administration’s policy focus on climate and racial equity.
Yet these results show that the trend for ESG integration had in fact started well before Biden’s election. The election actually occurred in a context where ESG integration in North America had already started responding positively to different factors.
We identified in previous research that ESG, S and E pillars performed strongly after they were triggered by the Covid-19-related stress in the equity market. While the Governance pillar initially lagged, it emerged as the most resilient during the crisis. However, since the election, the Governance momentum has slightly faded, while the Social and Environmental pillars have renewed their upward trends, although they have not yet regained pre-pandemic levels.

Emissions and Energy
According to the 2020 report of the International Energy Agency, CO2eq emissions in the US decreased between 2018 and 2019. In fact, in 2019, the US showed the largest country decline in energy-related CO2eq emissions, thanks to its increased use of natural gas for power generation as opposed to coal.
However, our analysis shows (Figure 2) that this was not priced into the equity markets at that time with the Emission & Energy sub-pillar continuing to deliver negative performance. Interestingly, since Joe Biden’s election in November 2020, a turnaround has occurred: investors are now moving towards companies that limit their emissions.

Growing influence of the social pillar in North America
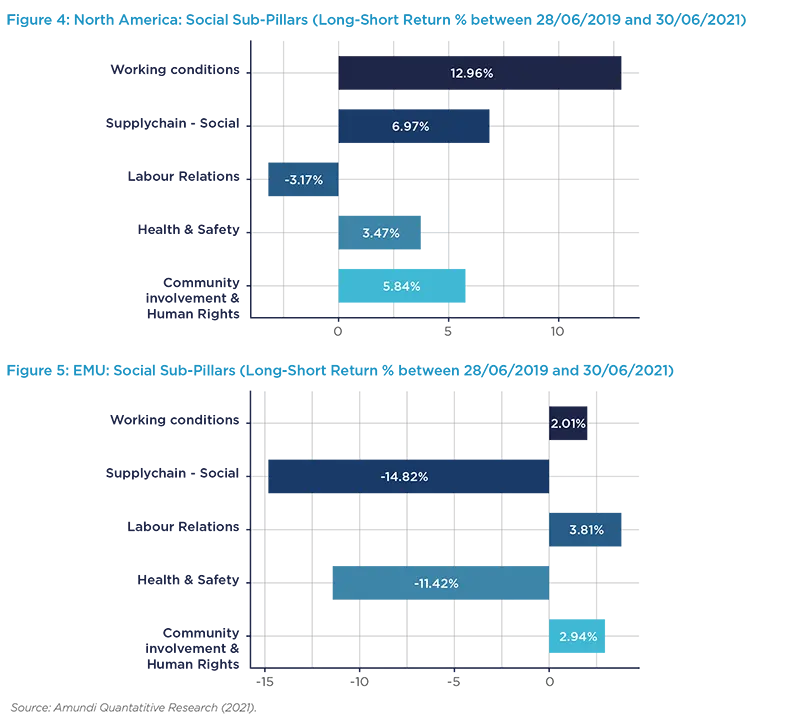
Recent studies (Lepetit & Sekine, 2020) have shown the Social pillar emerging in North America as it outperformed other ESG metrics in the first quarter of 2020. When analysing returns in the MSCI North America universe over the period, and in particular the individual sub-pillars making up the Social metric, it can be observed (Figure 4) that Working Conditions have been particularly valued by investors, rewarding companies who scored well on this aspect. This phenomenon does not appear to be coincidental. The Covid-19 crisis triggered deep uncertainty in North American labour markets, traditionally perceived as fairly flexible, raising fears of unemployment for millions of workers. In this context, companies who took a stance on the matter, such as announcing no redundancies, sent a positive signal to stockholders.
Also performing well since 2019 are the Supply Chain - Social and Community Involvement & Human Rights pillars, which indicates that the well-being of employees, but also of other stakeholders, are also being prioritised by investors.
However, whilst the Social pillar was the outright winner in North America in the first quarter of 2020, the trend did not persist across the rest of the year, although it has recently rebounded. In EMU, we witness a similar trend, although the Social pillar was less prominent when the pandemic hit financial markets. Here a slightly negative trend continued throughout the remainder of the period examined. In contrast to North America, the Working Conditions sub-pillar is not a dominant driver of performance in EMU and the Supply Chain – Social and Health & Safety sub-pillars significantly underperformed across the period of analysis, illustrating divergent domestic laws as well as differing investor focus, particularly concerning recent supply-chain controversies within EMU.
Better governance bolsters financing
One outcome of the pandemic was the increased requirements from corporates for external capital financing. Analysis (Halling et al. 2020) indicates that only 5% of capital raised came from equity compared to bond issues in the US.
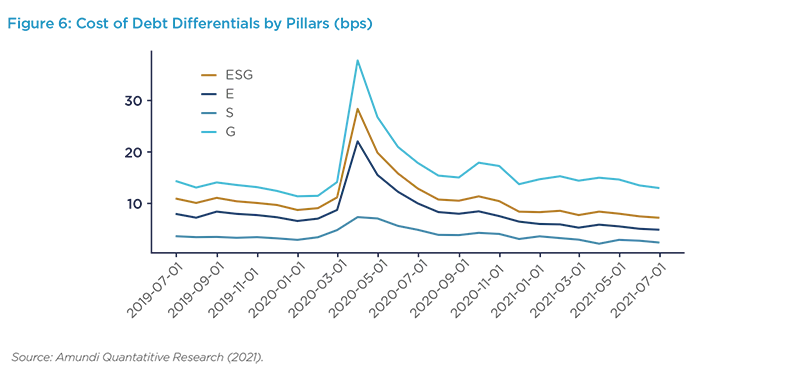
Extending our research to credit issues, we find that governance is the key differentiator and this was particularly apparent during the Covid-19 outbreak when the cost of debt spiked (Figure 6).
Since March 2020, governance has become a powerful discriminating feature where companies with good governance have been rewarded by the market with lower cost of debt, whilst the reverse has been true for poorly governed companies.
Focus on Emerging Asia
ESG in emerging markets is a thorny issue and these markets are often faced with strong challenges on various sustainability aspects. Past studies (Odell and Ali, 2016) have showed that weak institutions or uneven regulatory regimes may be responsible for social concerns. On the environmental front emerging markets are more exposed to climate change, but also to resource scarcity challenges and local pollution. Standards of governance and levels of disclosure compared to developed markets are also instrumental.
In this update, we extend our analysis to emerging markets, concentrating on Emerging Asia, however we revise the selected break-points to account for the earlier arrival of the Covid-19 pandemic in Asia compared to Europe and North America. A one-day time lag is also applied between North American and EMU to reflect the reaction lag in EMU due to the time difference between the two regions.
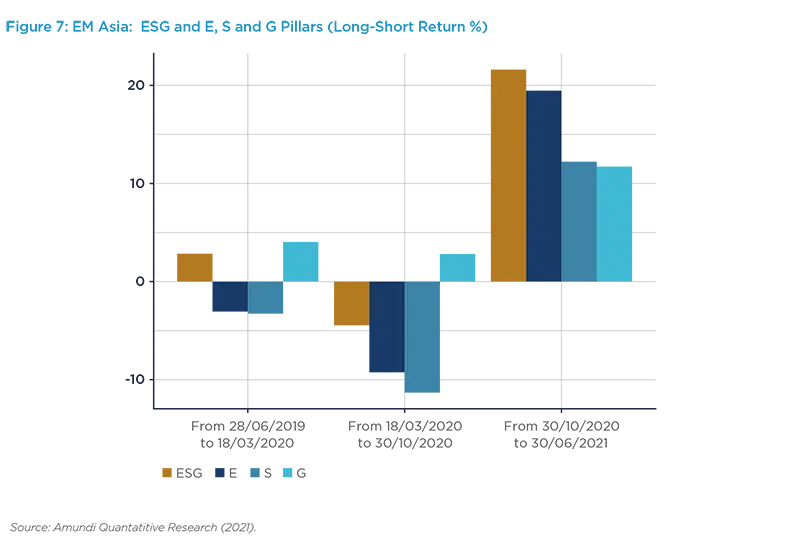
Similarly to EMU and North America, we witness that Governance has been the most resilient pillar during the Covid-19 phase (Figure 7) corroborating the idea that investors are particularly focused on this area. Interestingly the outstanding contributing sub-pillar within governance was Ethics, starting before the Covid-19 outbreak, but continuing thereafter. This may highlight growing concerns over this theme in Emerging Asia. We should not forget that the Covid-19 period also coincided with major supply-chain disruptions, which shed light on complex international networks, but also on unequal working conditions, raising ethical concerns.
The pattern of growing ethical concerns in Emerging Asia alongside the contrasting pricing of supply chain considerations in Europe and North America raises questions over the social and human aspects of production processes and is something we plan to study in more depth in the future.
It should be noted that the number of new Covid-19 cases remained fairly contained in Asia during the last quarter of 2020, compared to other regions that were hit by new waves. Nevertheless all pillars bounced back strongly in Emerging Asia in the most recent period, with some hypothesis that the Biden election may have been of significant help in relieving market uncertainty, which may have reinforced risk appetite, particularly from western investors who may have seen in Emerging Asia a new market to conquer. These flows benefited the ESG dimensions in the region.
Working Paper - ABSTRACT
The purpose of this paper is to appraise recent ESG trends in global equity markets. It contributes to a broader research project started at Amundi in 2014 on the relevance of ESG. Since the latest update in 2019, we have lived through a global pandemic that profoundly reshaped the global economy and society, and an eventful change of leadership in the United States. The aim of this paper is to analyze the changes in ESG trends since our latest update in June 2019. We work on the North American and EMU universes and, for the first time in our research series, also shed the light on Emerging Asia market. We identify that a presumed “Biden effect”, assumed to be supportive for ESG performance in North America, was actually anticipated earlier by investors and rooted in the fertile ground of rising ESG awareness. This being said, Joe Biden’s election may have fueled some momentum for the Emissions & Energy component of the Environmental pillar on both sides of the Atlantic at the end of 2020. In addition, we previously showed that the Social pillar in North America had already caught ESG investors’ attention following the market stress caused by the Covid-19 outbreak. Our results also demonstrate the Social pillar’s strong performance in North America since the end of 2020. Additionally, we show that companies with better Governance have been the most resilient in terms of performance during the pandemic’s troublesome market environment, independently of the region considered. In North America, employing credit market data, we demonstrate that these firms also benefited from a lower corporate cost of debt. In Emerging Asia, we have witnessed strong ESG performance since the end of 2020. Finally, employing a predictive non-linear framework, our results support ESG as a serious candidate risk factor not only in the EMU, but also in North America since 2019.










